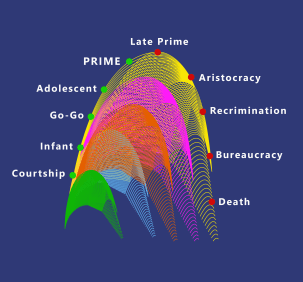
As organizations grow and age they progress through predictable lifecycle stages. Each stage brings increased organizational complexity as well as new and unique challenges. Strategy, structure, levels of delegation, goals, rewards systems and methods of operating usually differ quite markedly in each stage of the organization lifecycle. How well or how poorly leadership addresses the challenges and demands of each stage will determine the success or failure of the organization.
The following is a brief description of each of the 10 stages of the corporate lifecycle:
- Courtship
- The organization is not yet born
- There is excitement and unrealistic thinking
- The founder is building commitment
- Infant
- Lack of cash
- If undercapitalized the organization will chase any and all sales opportunities
- Lack of sales
- The organization may sell at a loss to generate cash
- Lack of experience
- The organization makes excessive commitments
- Go-Go
- Founder’s Trap – one person show
- Unfocused – spread too thin
- Opportunity driven
- Unclear priorities because everything is a priority
- The organization believes that ‘more is better’
- Strategic misalignment – mission, structure, systems, processes and rewards are usually not mutually supportive
- Adolescent
- Conflict between we and they – new and old
- Premature aging (loss of flexibility)
- Confusing structure
- Founder has difficulty delegating
- Professional managers are hired and encounter resistance
- Founder fears loss of control
- PRIME
- The organization is growing and profitable
- New ‘infants’ are spun off
- Success may breed complacency
- Measurements focus on the present value of past decisions
- Inadequate bench strength
- Late Prime
- Finance introduces controls for short term financial results
- The organization is becoming complacent
- Although it is not yet obvious the ‘aging’ process has begun
- Aristocracy
- Not making waves becomes a way of life.
- Outward signs of respectability take on enormous importance.
- The organization acquires companies rather than incubating startup businesses.
- Recrimination
- Witch-hunts become prevalent
- Back-stabbing becomes commonplace
- The customer is effectively a nuisance
- Bureaucracy
- The Bureaucracy is survival oriented
- There are policies for everything
- The written word is worshipped
- If the organization is important to the economy and the government has socialistic tendencies the organization will be put on life support (taxpayer dollars)
- Death
- The organization is bankrupt
